 Figure 2
Figure 2
david.spinks@aeat.co.uk
As the deadline grows ever closer, it becomes more and more important to prioritise Year 2000 investigative and remedial work and this evidence as to the areas at risk should help companies in focussing their efforts. It must be stressed, however, that all Year 2000 work is an exercise in risk management - no organisation can guarantee 100% compliance.
Note that the information given here is an indication of the types of problems being found. It is not intended to be all encompassing. Its aim is to provide those with responsibility for ensuring the continuing operation of buildings and process systems through the Millennium date change, a view of the actual problems being found elsewhere. Through this, the objective is to provide a shortened learning curve for those who have not yet completed their project and a means to double check systems where th e project is thought to be complete.
The data has been provided by the following organisations, whose contributions are here acknowledged:
· AEA Technology
· BSC Consulting
· ERA
· IBM
· ICS
· Real Time Engineering
· The Houndscroft Partnership
The contributors have provided data on problems that they have found consistently in their investigations of companies and their equipment. Exceptional cases and applications specific to a particular process in a particular company are not included. Fo r legal and commercial reasons, the sources of each piece of data are not publicly available. However, the list is of real cases and all data is auditable and traceable by Action 2000. All business and trade names have also been removed.
It is intended to keep the database updated and new entries would be welcomed. There is a standard format for the provision of data that can be obtained from Action 2000.
It is generally useful to divide embedded systems into three areas: The first is those that are microcontroller based. These are extremely simple devices such as door chimes, etc which are not programmable and almost never have any date functionality. There are millions of these about, but they can be largely dismissed.
Next come microprocessor based systems which are usually programmable and may indeed have some date functionality. Earlier experiences from many sources have suggested that Year 2000 problems occur in between 1% and 6% of microprocessor based embedded systems.
At the top comes those more complex systems which include a `computer'. (By `computer', we here mean either PCs or other conventional hard-disk based computers.) The probability of Y2k problems for these systems has been found to be significantly.
Based on the latter two categories, it is helpful to divide the data into the two relevant sections: Those systems that involve a `computer', and those that don't.
Roughly 40% of the entries in the database are `computer' based and in all these cases, the computer is a significant (but not necessarily the only) problem. The other 60% were systems using a range of nondiscrete computer technologies.
For the non-computer data we have recorded, the equipment type categories in the survey were:
· Access Control · Logging /
· Building Mgmt Monitoring
Sys · OTHER
· Complex Process · PLC
· Date Coding · SCADA
· DCS · Smart
· Fire Control Instruments
· HVAC · Stand Alone
Instrument
After combining similar categories together to simplify the data, the following statistics show the areas reported with most problems in non`computer' based systems (in decreasing order):
· Calibration, Monitoring, Data Logging, Detectors, Analysers
· Building Management, including HVAC, fire and security systems
· Manufacturing and process systems (SCADA, PLC, DCS)
· Telecoms and Networking
· Other
 Figure 2
Figure 2
(Note. The percentages in the diagram indicate the proportions of problems found by our research in each area. This may or may not align with the situation in particular companies or industries)
Looking at those systems which DO contain a `computer', then we find a not dissimilar distribution of problems after dividing the items into:
· Building Management Systems (including fire and security
control)
· Manufacturing and Process control systems
· Logging and monitoring equipment
· Others
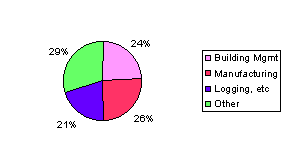 Figure 3
Figure 3
In terms of the date which caused the problem, 71% were the millennium rollover, 9% were a leap year problem, 6% were multiple date problems and the remainder were either obscure other dates or unknown.
Detailed survey results begin on the next page. `Non-computer' systems are listed first and they are listed in alphabetical order of Equipment Type.
Remember that although the survey results describe the impact of the system failure, this is for a specific case and the business impact of the same failure may be very different in another industry.
Equipment Type Industry Sector PC or Computer based No Case 1 Access Control ALL System Age 10-15 years Application Card access control system for site and internal departments Description of the Problem System fails at rollover. Access barred. How was it Identified Standard rollover test What was the Solution Replace Consequences for the SYSTEM System Stops Consequences of failure to the BUSINESS Security system inoperable. Additional manning required.
Equipment Type Industry Sector PC or Computer based No Case 2 Access Control ALL Application Intruder Panel Description of the Problem Does not recognise leap year, hence date becomes erroneous. Critical date is 29th February. This problem is experienced every leap year. How was it Identified Information supplied by manufacturer. What was the Solution Correct date on 1st March. (As will have been done in previous years) Consequences for the SYSTEM Cosmetic Consequences of failure to the BUSINESS Incorrect date logging.
Equipment Type Industry Sector PC or Computer based No Case 3 Building Mgmt Sys ALL Application Fire Alarm Panel Description of the Problem System crashes on rollover, can be reset in year 2000, but doesn't recognise leap years. Critical date 01/01/2000. How was it Identified Manufacturer supplied information. What was the Solution Replace equipment. Consequences for the SYSTEM System Stops Consequences of failure to the BUSINESS Building is left unprotected if system is not reset immediately after roll-over.
Equipment Type Industry Sector PC or Computer based No Case 4 Complex Process Communications Application A multi-site organisation has a multi-service bandwidth manager with management system which is non-compliant. Description of the Problem The vendor advised the client not to allow the system to roll into the next century as 'unstable or unpredictable results could occur'. The cause is that the management software application has not been designed to take account of four digit dates or the year '00'. How was it Identified It was recommended that the client contact the vendors of their systems. As a result of this contact, the vendor advised the client that there was a major problem with the management software system. What was the Solution The management system is completely non-compliant. The solution is to replace the management system with a system which is compliant. Consequences for the SYSTEM System Stops Consequences of failure to the BUSINESS Critical
Equipment Type Industry Sector PC or Computer based No Case 5 Date coding Manufacturing System Age less than 5 years Application Date coding (ink jet) of finished product Description of the Problem Unit fails to roll coding date forward correctly once code date is in Year 2000 (i.e. failure as soon as forward date hits Year 2000) How was it Identified Within standard rollover test procedure What was the Solution Replacement PROM Consequences for the SYSTEM Erroneous Result Consequences of failure to the BUSINESS Serious problem if not rectified. Manual date entry possible (and would have worked) but given the number of units this would present major difficulties. Other 2 attempts required to get correct replacement PROM Always test replacements!
Equipment Type Industry Sector PC or Computer based No Case 6 Date coding Manufacturing System Age approx. 7 yrs Application Date coding (laser) of finished product Description of the Problem a) Date fails to roll over correctly thro' millennium transition b) two ways to format date (with spaces & without). Rollover test result depends on format: one fails & the other is OK. How was it Identified a) through standard rollover test b) unit replaced as a result of in-service failure was rechecked for compliance and failed as service engineer had used alternative format for date entry (previously unknown). What was the Solution Replacement PROM Consequences for the SYSTEM Erroneous Result Consequences of failure to the BUSINESS
Equipment Type Industry Sector PC or Computer based No Case 7 DCS Oil & Gas System Age 6 years Application DCS control system control for petrochemical plant Description of the Problem Online rollover to Year 2000 How was it Identified During testing. Offsite testing on a testbed was performed with satisfactory results. Upon testing of stations on site, control was no longer possible after the system had rolled over to Year 2000. It was not until this problem was evident on three of the four operating stations was testing aborted. What was the Solution No known workaround. Plant had to be operated from one station until problem could be rectified Consequences for the SYSTEM System Stops Consequences of failure to the BUSINESS Near catastrophic. Limited reliability and operability of plant. Reduced production
Equipment Type Industry Sector PC or Computer based No Case 8 DCS Process System Age 8 years Application DCS Control System controlling smelter plant Description of the Problem Rollover to year 2000 System on reboot reverted to incorrect date How was it Identified Power down rollover test What was the Solution Replace battery backup Consequences for the SYSTEM Erroneous Result Consequences of failure to the BUSINESS Loss/corruption of trend data
Equipment Type Industry Sector PC or Computer based No Case 9 Fire Control ALL System Age Oct-1998 Application Fire Alarm Panel - sounds alarm when triggered. Description of the Problem Date advances from 31/12/99 to 01/01/100. Critical date 01/01/2000. How was it Identified Rollover Testing What was the Solution Client informed. Does not affect operation of system, only reporting. Consequences for the SYSTEM Cosmetic Consequences of failure to the BUSINESS Other Unit continues to function, but displays incorrect date. When powered down returns date 01/01/00 or 100. Unit accepts invalid dates.
Equipment Type Industry Sector PC or Computer based No Case 10 Fire Control ALL Application Fire alarm control panel - sounds alarm. Description of the Problem Fire alarm malfunction on rollover- alarm raised. Critical 01/01/2000. How was it Identified Testing. What was the Solution Software upgrade. Consequences for the SYSTEM Erroneous Result Consequences of failure to the BUSINESS Would lead to building being evacuated.
Equipment Type Industry Sector PC or Computer based No Case 11 Fire Control ALL Application Fire Alarm Panel. Description of the Problem Does not recognise year 2000 as a leap year. Critical date 29/02/2000. How was it Identified Manufacturer has supplied information. What was the Solution Manually change date on 1st March 2000. Consequences for the SYSTEM Cosmetic Consequences of failure to the BUSINESS Other Panel does not recognise any leap year.
Equipment Type Industry Sector PC or Computer based No Case 12 Fire Control ALL System Age 10 Application Central fire alarm monitoring Description of the Problem Clock will revert to1900 with power switched on. Will not recognise leap year. Current day /time incorrectly displayed. Elapsed time fault monitoring functions may not recognise genuine fault during transition 1999 to 2000 How was it Identified Identified by manufacturer. What was the Solution No fix available. New unit purchased. Consequences for the SYSTEM System Stops Consequences of failure to the BUSINESS Inability to remotely monitor in-plant/office fire alarm systems. Could be even more critical if process systems fail etc during rollover and manning will also be minimum during this period.
Equipment Type Industry Sector PC or Computer based No Case 13 HVAC Finance System Age Feb-1998 Application Communications Room Air Conditioning unit. Description of the Problem Date advances from 31/12/99 to 01/01/99. Critical date is 01/01/2000 Unit continued to function normally but reported date incorrectly. How was it Identified Rollover Testing What was the Solution Upgrade to compliant version of software. Consequences for the SYSTEM Cosmetic Consequences of failure to the BUSINESS
Equipment Type Industry Sector PC or Computer based No Case 14 HVAC ALL System Age 6 Application Package Boiler Control System local and remote Description of the Problem Hardware and software How was it Identified Z180 Microprocessors found during physical examination and 2 digit date found when examining code ( assembler ?) What was the Solution Solution not yet known as manufacturer not now in business Consequences for the SYSTEM System Stops Consequences of failure to the BUSINESS Failure would result in no bulk oil supplies to a major works as steam is used to preheat heavy oil for distribution (5 x 10,000 tonne tanks pumped at 50t /hour)
Equipment Type Industry Sector PC or Computer based No Case 15 HVAC ALL Application Air Conditioning/Heating Controls Description of the Problem Loss of control of HVAC system. Critical date 01/01/2000. How was it Identified Manufacturer aware, confirmed through testing. What was the Solution Upgrade software. Manufacturer supplying free upgrade. Consequences for the SYSTEM Erroneous Result Consequences of failure to the BUSINESS Potentially catastrophic.
Equipment Type Industry Sector PC or Computer based No Case 16 HVAC ALL Application Controller with logging capabilities.(Outstation) Description of the Problem Potential loss of historic data. Critical date 01/01/2000. No affect on control operation. How was it Identified Rollover Testing. What was the Solution Download the data prior to roll over. Consequences for the SYSTEM Cosmetic Consequences of failure to the BUSINESS
Equipment Type Industry Sector PC or Computer based No Case 17 HVAC ALL Application Controlling & Monitoring. (Outstation) Description of the Problem Loss of control of Air conditioning. Critical date 01/01/2000. How was it Identified Rollover Testing. What was the Solution Replace microprocessor/ Replace equipment. Consequences for the SYSTEM Erroneous Result Consequences of failure to the BUSINESS Potentially catastrophic if A/C does not function in communications areas.
Equipment Type Industry Sector PC or Computer based No Case 18 HVAC Manufacturing System Age approx. 10 years Application Control of mechanical services and air conditioning equipment Description of the Problem Controller fails on first power-up after rollover (31/12/99-1/1/00) irrespective of whether rollover was with power on or How was it Identified Standard rollover test What was the Solution Replacement PROM Consequences for the SYSTEM System Stops Consequences of failure to the BUSINESS Nuisance failure of services to manufacturing plants resulting in significant downtime. Actual date unimportant so workaround possible.
Equipment Type Industry Sector PC or Computer based No Case 19 Logging / Monitoring ALL Application Data Tape Recorder. Description of the Problem Critical date 01/01/2000. How was it Identified Manufacturer supplied information. What was the Solution Software upgrade. Consequences for the SYSTEM System Stops Consequences of failure to the BUSINESS
Equipment Type Industry Sector PC or Computer based No Case 20 Logging / Monitoring ALL Application Water leak detection. Description of the Problem Non reporting of leaks / fire alarms. Potential false alarms. Critical date 01/01/2000. How was it Identified Manufacturer supplied information. What was the Solution Upgrade microprocessor. Consequences for the SYSTEM Erroneous Result Consequences of failure to the BUSINESS Non reporting of leaks could cause major damage with long down times. False alarms would cause systems (e.g.. air conditioning) to be closed down- potentially catastrophic if supporting Comms room.
Equipment Type Industry Sector PC or Computer based No Case 21 Logging / Monitoring Manufacturing System Age 5 Application Portable bearing monitoring data collector Description of the Problem Statements from Manufacturer i.e. not compliant How was it Identified Information received on request What was the Solution Firmware upgrade to each data collector plus software upgrades to central operating system Consequences for the SYSTEM System Stops Consequences of failure to the BUSINESS Some inconvenience to maintenance activities
Equipment Type Industry Sector PC or Computer based No Case 22 OTHER Media Application Tracking system used on 6m and 8m satellite dishes. Used to position satellite dishes which provide uplinks to communication satellites in geostationary orbit. Description of the Problem The tracking system rolls over into the next century and the year '00' is interpreted as an invalid date. Knowledge of the date is essential to finding the position of the satellites. How was it Identified System was noted to be date aware and a spare was tested for compliance. What was the Solution There are three possibilities: 1) Upgrade the tracking system; 2) Use alternative transmission means, such as fibre optics; 3) Transmit using smaller satellite dishes on higher power. Consequences for the SYSTEM System Stops Consequences of failure to the BUSINESS It will not be possible to broadcast TV signals. Viewers will go elsewhere for their entertainment; revenue from advertising is tied to audience figures. Inability to broadcast daily news programs would be a breach of the broadcast licence in some instances.
Equipment Type Industry Sector PC or Computer based No Case 23 OTHER Communications Application Multi-site organisation has a packet switching mechanism to allow medium speed data communications. Description of the Problem Each communication node in the network has a real time chip in the node firmware. The firmware only 'sees' two digit dates. The system will not function correctly if allowed to roll into the next century. The packet switching management system is a supervisory level system with non-compliant operating system in conjunction with a non-compliant application software. How was it Identified Consultants recommended that the client contact the vendors of their systems. As a result of this contact, the vendor advised the client that there was a major problem with the network and management system. What was the Solution The packet switching device will have its internal clock wound back by 28 years to synchronise days of the week and leap years. The packet switching management system will be completely decommissioned. No fix has been identified for the application system although the operating system could be upgraded. Consequences for the SYSTEM Erroneous Result Consequences of failure to the BUSINESS The management system is the key to determining fault location, performance metrics, and event reporting. Without the management system, it will be difficult to manage with faults, and alterations will take longer to deal with, thus impacting network resilience. Other Any data communications network with a management system may be prone to this type of problem.
Equipment Type Industry Sector PC or Computer based No Case 24 OTHER ALL System Age 5 years Application Car Park Management System Description of the Problem Dates after 31/12/99 not handled correctly How was it Identified Manufacturers advice What was the Solution Replacement of hardware and software Consequences for the SYSTEM Erroneous Result Consequences of failure to the BUSINESS Loss of revenue, lack of car-parking causing traffic congestion, safety - if car park egress not possible or restricted.
Equipment Type Industry Sector PC or Computer based No Case 25 OTHER OTHER Application Data Logger. Receives input from plant sensors, then monitors and records this information. It triggers high and low level alarms if changes in the state of systems require attention. Description of the Problem Some software versions are non-compliant in that they fail to log data after 31/12/99. Monitoring of plant equipment/processes will, therefore, not be possible. How was it Identified Manufacturer knows which software versions are at risk. It is necessary to remove the processor board and read the serial number from the EPROMS to check which version is installed on the individual items. What was the Solution Software upgrade where necessary - by replacing the EPROMS. Consequences for the SYSTEM System Stops Consequences of failure to the BUSINESS In the event of an emergency, output from the logger is used by regulators for post-incident analysis. Loss of this system could lead to fines being imposed or plant shutdown being ordered..
Equipment Type Industry Sector PC or Computer based No Case 26 Chart recorder. OTHER System Age 2 yrs Application Plots radiation levels, as a function of time, beside a liquid waste disposal drain. The information is printed out and date stamped at midnight every day. It is required for regulatory purposes in case radiation levels exceed acceptable limits. Description of the Problem For models sold before 1996, the recorder will stamp print outs with incorrect dates after 31/12/99. This will lead to regulatory non-compliance. How was it Identified Identifying serial numbers and contacting suppliers. What was the Solution The recorder can be replaced with a newer model. Alternatively, printouts can be manually date stamped. Consequences for the SYSTEM Erroneous Result Consequences of failure to the BUSINESS Possible fines imposed by regulators.
Equipment Type Industry Sector PC or Computer based No Case 27 Vibration monitor on rail network. Rail Transport Application If train wheels have a flat spot, or axles are damaged, the rail will vibrate due to the uneven load distribution. These vibrations are detected by monitors on the rails, allowing faults to be identified. Description of the Problem There are two models of this system: Mark 1 will fail to operate completely after 09/09/99 due to the fact that 999 was used as an end of file marker; Mark 2 will operate until the end of 1999, but its internal clock will fail to rollover into the next century. How was it Identified Supplier information was referred to initially, rollover testing was then carried out. What was the Solution Both systems were rolled back to determine which, if any, of the previous leap years it would be possible to use. The Mark 2 systems cannot be rolled back to a date prior to system installation, for example 1996. Mark 1 systems can be rolled back to any date, but will fail again once their internal clock reached 9/99. Consequences for the SYSTEM Erroneous Result Consequences of failure to the BUSINESS Catastrophic if a problem, which subsequently leads to an accident, cannot be identified.
Equipment Type Industry Sector PC or Computer based No Case 28 Voice Comms. Rail Transport Application System used for voice and data communications between train drivers and signallers. Description of the Problem Before updating the time, the management processor sets all of its internal registers to zero, and monitors the status of them afterwards. If the status of one or more registers is still zero, this is interpreted as message not received. The processor will await the arrival of a valid signal before updating the time and date. So, effectively, it will cease to function for one year, then resume normal operation on 01/01/01. How was it Identified Discussions with the users and then structured interview with the equipment manufacturer. The manufacturer was unable to answer all questions satisfactorily and during follow-up work discovered the error. What was the Solution The equipment manufacturer must provide a software upgrade. Consequences for the SYSTEM System Stops Consequences of failure to the BUSINESS If information gets out of sequence, chaos will ensue. Train delays will occur, and there will be increased risk of rail accidents. The cost of this could be considerable. There will also be regulatory problems as, in the event of an emergency, logs and sequencing information is needed for post-incidence enquiries.
Equipment Type Industry Sector PC or Computer based No Case 29 Photocopier Support Services Application Photocopier Description of the Problem Does not rollover. Manual set to 01/01/00 required How was it Identified Manufacturer's advice What was the Solution Manual set or replace if required Consequences for the SYSTEM Cosmetic Consequences of failure to the BUSINESS
Equipment Type Industry Sector PC or Computer based No Case 30 Automatic tape machine. Media Application Selects a tape from an archive library, places it in a player, and switches to that particular player at the required moment. Once the tape in no-longer required it is removed and placed back in the archive. Description of the Problem The bespoke software used by the machine is non-compliant. It does not recognise 2000 as a valid date and will not turn on the player. This will disrupt the broadcast. How was it Identified The system manufactures identified the problem and are offering an upgrade. What was the Solution The material to be broadcast can be played directly from a prerecorded source. If this cannot be located, standby films must be played. TV engineers will be required to by-pass the tape machine. Consequences for the SYSTEM System Stops Consequences of failure to the BUSINESS Advertising revenue is closely tied to viewing figures. Anything which disrupts the viewing pattern has an immediate impact on revenue. Other This is a relatively complicated machine having three computers to control its function.
Equipment Type Industry Sector PC or Computer based No Case 31 Ultrasound Medical Application Scanning equipment (Ultrasound). Description of the Problem Gestation period calculation error. Critical date 01/01/2000. How was it Identified Manufacturer supplied information. What was the Solution Upgrade equipment. Consequences for the SYSTEM Erroneous Result Consequences of failure to the BUSINESS Birth date miscalculations
Equipment Type Industry Sector PC or Computer based No Case 32 Audio Monitor Medical System Age various Application Audio Monitor. Description of the Problem Equipment functions if used in isolation. If connected to a PC requires a microprocessor upgrade to become compliant. Critical date 01/01/2000. How was it Identified Manufacturer supplied information. What was the Solution Establish whether units are used in isolation or as part of system. If part of system upgrade. Consequences for the SYSTEM Cosmetic Consequences of failure to the BUSINESS
Equipment Type Industry Sector PC or Computer based No Case 33 Weighing machine Manufacturing System Age 5 - 10 years Application Weighing of finished product Description of the Problem Apparent failure (ref 2 below) to recognise leap year. Jumps from 28/2/00-1/3/00 How was it Identified Roll over from 28/2/00 to 29/2/00 fails. Part of standard test What was the Solution PROM replacement Consequences for the SYSTEM Erroneous Result Consequences of failure to the BUSINESS 1. Possible breach of statutory requirements if data used to meet average weight legislation. 2. Some versions count year transitions to identify leap years. Other Testing can (and did) upset this procedure: it is important to ensure that the system is left in the correct state after test.
Equipment Type Industry Sector PC or Computer based No Case 34 Telephone Communications Application PBX telephone software. Description of the Problem The phones worked on rollover to 1st January 2000 but the management software system failed. This would affect billing, fault logging, volume of calls monitoring etc. How was it Identified The problem was identified during rollover to 1st January 2000. What was the Solution Both the software and hardware which together comprise the PBX management system are being replaced. Consequences for the SYSTEM Erroneous Result Consequences of failure to the BUSINESS Major nuisance if the management of the internal phone system fails. The phones will continue to work but faults will not be identified for rectification.
Equipment Type Industry Sector PC or Computer based No Case 35 Gas detector Oil & Gas Application Personal Gas detector and associated software Description of the Problem The gas detector's functionality and alarm worked on all identified critical dates. The applications software failed to rollover correctly on the following identified critical dates:31-12-99 to 01-01-00; 28-2-00 to 29-2-00; 29-2-00 to 1-3-00; 28-2-04 to 29-2-04; 29-2-04 to 1-3-04. The date displayed was incorrect. How was it Identified The problem was identified during rollover testing at the vendor site. What was the Solution No decision has yet been made about dealing with this problem, as the client was determining the importance of the application software to the various business units before corrective actions were identified. Consequences for the SYSTEM Cosmetic Consequences of failure to the BUSINESS Nuisance
Equipment Type Industry Sector PC or Computer based No Case 36 Fuel Pump Oil & Gas Application Fuel Pump Description of the Problem Year does not rollover. Leap years are not recognised. 31/12/xx. How was it Identified Testing confirmed, however manufacturer & client aware. What was the Solution Client "working around" fault. Corrects date on 1st January each year Consequences for the SYSTEM Cosmetic Consequences of failure to the BUSINESS
Equipment Type Industry Sector PC or Computer based No Case 37 PLC Manufacturing System Age 2 years Application PLC-based control system Description of the Problem Unit passes all Y2K tests but at transition from 31/12/03 - 1/1/04 reverts to 1/1/00 How was it Identified Testing by test engineer What was the Solution Replacement PROM Consequences for the SYSTEM Cosmetic Consequences of failure to the BUSINESS
Equipment Type Industry Sector PC or Computer based No Case 38 PLC Process System Age 4 years Application PLC hardware Description of the Problem Does not process dates after 31/12/99 correctly How was it Identified Manufacturers advice What was the Solution Problem to be ignored Consequences for the SYSTEM Cosmetic Consequences of failure to the BUSINESS Year rolls over from '99' to '01'
Equipment Type Industry Sector PC or Computer based No Case 39 PLC Manufacturing System Age Unknown Application CNC Milling Machine. The system is used to manufacture aircraft parts and is controlled by PLCs. Description of the Problem - At the 31/12/1999-1/1/2000 transition, the PLC's BIOS resets from 31/12/99 to 4/1/1980; - NC program data with the current date (1/1/2000) is then downloaded from the DNC network; - There will now be a date conflict between the downloaded NC data and the internal date. How was it Identified Information from supplier states that current 'x' series PLC and operating system software are BOTH non-compliant. Analysis and rollover testing confirmed the non-compliance of these PLC and this version of the operating software. What was the Solution Upgrade of operating system in 3 stages. Consequences for the SYSTEM Erroneous Result Consequences of failure to the BUSINESS Confusion over NC files which are downloaded over the site network due to date discrepancies. There are three of these machines dedicated to the same task, all are identical and therefore consequence of failure is increased threefold. As far as known, these are the only machines available to manufacture the above aircraft parts to the proven method at this site.
Equipment Type Industry Sector PC or Computer based No Case 40 PLC OTHER Application Robot used to change air filters in a restricted area. May be used in automatic mode, controlled by a PLC. It can also be used in manual mode, however the operator relies on the PLC to receive information from sensors on the robot arm. Fully manual operation is not possible. Description of the Problem PLCs running certain versions of the operating system will fail to rollover into the next century correctly. This will disable the robot. Problems will not be experienced immediately as the robot is not in constant use. However failure to correct the problem would seriously impair production. The operator terminal used to program the PLC is non-compliant as is the programming software. It may be difficult, if not impossible to roll the PLC system clock back and, if necessary kit changes cannot be made, production will be stopped. How was it Identified Site investigation and discussions with the manufacturer. What was the Solution Currently not resolved. Complete replacement of the PLC is being discussed. As a temporary measure, full manual operation will probably be investigated. Consequences for the SYSTEM System Stops Consequences of failure to the BUSINESS Production must stop. Unless a solution is found regulatory noncompliance would follow. Other Workarounds, such as operating staff manually changing filters, are not possible as persons cannot be admitted to the necessary areas.
Equipment Type Industry Sector PC or Computer based No Case 41 SCADA Manufacturing System Age 6 Application Supervisory control & archive data for production process Description of the Problem Loss of comms to discrete control functions Failure of archiving process data due to 2 digit dates How was it Identified Partly identified by manufacturer's own test and warning to users and by on site audit by manufacturer What was the Solution Fix installed by manufacturer Consequences for the SYSTEM System Stops Consequences of failure to the BUSINESS Loss of heating models for process. Unusable product. Loss of process data for quality control and QA. Unable to sell product.
Equipment Type Industry Sector PC or Computer based No Case 42 SCADA Manufacturing System Age 2 Application Monitoring of high frequency welding equipment Description of the Problem All datalogging after Jan 1 2000 would be erased as `old' data How was it Identified Information from website. What was the Solution A software patch is available and will be installed by original supplier of equipment. This original supplier had been unaware of the problem and consequently will need to fix several hundred similar systems worldwide Consequences for the SYSTEM System Stops Consequences of failure to the BUSINESS Loss of historical trending data and traceability for QA. Other This emphasises the importance of not taking information provided by vendors at face value, but to continually revisit manufacturers for updates.
Equipment Type Industry Sector PC or Computer based No Case 43 SCADA Manufacturing System Age 1-10 years Application Bought-in graphics/display package Description of the Problem Core functionality OK but some optional modules fail rollover test How was it Identified Manufacturer's rollover tests What was the Solution Upgrade or replace Consequences for the SYSTEM Cosmetic Consequences of failure to the BUSINESS Largely cosmetic (loss of data logging and trending info) but could be more serious in the event of major plant problems and lead to additional downtime
Equipment Type Industry Sector PC or Computer based No Case 44 SCADA Manufacturing Application SCADA system which provided an overview of the operation of some 250 systems in a manufacturing plant. Description of the Problem The system failed during the power down rollover test such that it would not start up again when power was re-applied. The system backup was restored and the system successfully reinitialised. How was it Identified The problem was identified during diligence testing, with the vendor present, to prove compliance of a system that the vendor had claimed was compliant. The test it failed on was the power down rollover test (i.e. letting the system roll over from 31st December 1999 to 1st January 2000 with the main power removed). The system would not start up again when power was re-applied. What was the Solution The problem was rectified immediately by the vendors. Software modifications were made. Consequences for the SYSTEM System Stops Consequences of failure to the BUSINESS If this failure happens on restarting the system after the millennium shutdown, and the system backup is not readily available to be restored, then this will result in significant downtime. Other Failure under test can be as serious an issue as year 2000 failure itself, and so adequate test planning which includes proven recovery procedures is essential.
Equipment Type Industry Sector PC or Computer based No Case 45 SCADA OTHER Application Used to control and monitor alarms. Alarms are time and date stamped when displayed on the chronological alarm list or sent to the printer. Description of the Problem Printouts would display incorrect dates after 31/12/99 as a result of non-compliant SCADA software. How was it Identified Technical discussions with equipment suppliers and reference to relevant documentation. What was the Solution Replace the SCADA software with fully Year 2000 compliant versions. Consequences for the SYSTEM Erroneous Result Consequences of failure to the BUSINESS In the event of an incident, such as fire, date stamped records may be needed for a post-incident enquiry. Should these details be inaccurate, regulatory problems could ensue. The business could be fined as a result of this.
Equipment Type Industry Sector PC or Computer based No Case 46 Smart instruments Manufacturing System Age 5 years Application Weighing of finished products (multiple weighers on network) Description of the Problem System fails to rollover correctly How was it Identified Standard rollover test What was the Solution Software update required Consequences for the SYSTEM Erroneous Result Consequences of failure to the BUSINESS Failure to meet statutory requirements for average weight legislation. Significant nuisance as manual operation difficult.
Equipment Type Industry Sector PC or Computer based No Case 47 Smart Instruments OTHER Application A multisite utility company has 1.2 million meters, (electronic and mechanical) with 30% electronic meters. A problem arose with the calibration equipment for the electronic meters. Description of the Problem On testing electronic meters and rolling through the dates post 2000, the calibration equipment 'stuck' at 2010. How was it Identified The problem was discovered unexpectedly during testing of electronic meters. The meters proved to be compliant but the test equipment was not. What was the Solution The calibration equipment was reset by the vendor and an upgrade patch inserted. Consequences for the SYSTEM System Stops Consequences of failure to the BUSINESS This caused a major logistical problem as a backlog of calibration checks built up. Other Any calibration kit must be tested for year 2000 compliance as well as the equipment it is checking.
Equipment Type Industry Sector PC or Computer based No Case 48 Smart Instruments Oil & Gas Application A smart density analyser uses a radio-active source as part of its measuring process. Description of the Problem The algorithm which compensates for the decay of the radio-active source gives erroneous results on rollover to 1st January 2000. How was it Identified The problem was identified during telephone call to the vendor to make initial enquiries regarding year 2000 compliance. What was the Solution It was initially thought that the solution would be to recalibrate the instrument on 31st December 1999 and to have the date entered of 1st January 2000, and then to recalibrate again on 1st January 2000. The manufacturer discovered however that doing two sequential recalibrations also caused major problems. The manufacturer is now offering users of the system an EPROM upgrade. Consequences for the SYSTEM Erroneous Result Consequences of failure to the BUSINESS In an operating process, this would raise alarms and possibly result in a costly process shutdown.
Equipment Type Industry Sector PC or Computer based No Caser 49 Stand Alone Instrument Medical Application Defibrillator. Description of the Problem On some models, if the reporting function is used and a report is generated in the 20th century, it is not possible to store reports generated in the 21st century. Does not recognise leap year. Critical date 29th February. How was it Identified Manufacturer confirmed. What was the Solution Upgrade software. Consequences for the SYSTEM Cosmetic Consequences of failure to the BUSINESS Does not affect operation of equipment only reporting functions
Equipment Type Industry Sector PC or Computer based No Case 50 UPS ALL Application UPS- Uninterruptible Power Supply. Description of the Problem Loss of remote data/ alarm logging. Critical date 01/01/2000. How was it Identified Information supplied by manufacturer & confirmed through testing. What was the Solution Upgrade microprocessor Consequences for the SYSTEM Erroneous Result Consequences of failure to the BUSINESS If external monitoring is utilised, may be catastrophic.
Equipment Type Industry Sector PC or Computer based Yes Case 51 Access Control ALL Application Site-wide building access control and security system Six connected controllers, at various site locations, controlling a network of card readers and keypads (supported by modems etc), printers and visual display terminals. Description of the Problem The control panel will rollover correctly from 28/02/00 to 29/02/00. However, if 29/02/00 is entered manually, it will default to 01/02/00. How was it Identified Technical discussions with supplier and reference to relevant documentation. What was the Solution The access control software will be upgraded and the control panels replaced. Consequences for the SYSTEM Erroneous Result Consequences of failure to the BUSINESS Nuisance, but may cause regulatory problems. Access to restricted areas may be controlled using a manual, paperbased system. However this is expensive and time consuming. Other Health and safety is the top priority. In this instance it is important for the system owner to know where personnel were working.
Equipment Type Industry Sector PC or Computer based Yes Case 52 Building Mgmt Sys ALL Application BMS Description of the Problem The system will operate correctly through the millennium rollover if the system remains powered. If the system is powered down, however, the date will revert to XX/XX/1900 How was it Identified Manufacturer claims not compliant, recommends upgrade to compliant system. What was the Solution Upgrade/ replace equipment. Consequences for the SYSTEM System Stops Consequences of failure to the BUSINESS Potential failure of air conditioning/ heating system, security systems etc.
Equipment Type Industry Sector PC or Computer based Yes Case 53 Building Mgmt Sys ALL System Age 1995 Application Swipe card system- Access control. Description of the Problem Will not allow access from 01/01/2000. Critical date 01/01/2000. How was it Identified Manufacturers supplied information. What was the Solution Both software and hardware upgrades maybe necessary. Consequences for the SYSTEM Erroneous Result Consequences of failure to the BUSINESS Will cause significant inconvenience to business. Other Some manufacturers are supplying free upgrades. Others are changing. Individual systems should be investigated.
Equipment Type Industry Sector PC or Computer based Yes Case 54 Building Mgmt Sys ALL System Age 6+ Application This is a building (energy) management system (BEMS) and comprises a master (communications unit) and a number of slaves (control units). The master is connected to each slave by means of an RS485 link and each slave controls various analogue and digital devices such as boilers, air-conditioning units, chillers etc. by means of an interface board. Depending upon the nature of the item controlled the board may be either analogue or digital. Programming the (master) communications unit is accomplished by means of, say, a hand-held unit or PC connected to the unit via. an RS232 link. The control units contain a keypad that allow them to be programmed with times and dates, type of functions to execute etc. Description of the Problem As dates in the next century cannot be set, date-based functional tests cannot be carried out. Therefore, any problems that may be caused by this situation will not be known until the next century. How was it Identified Control units: A series of power-on and power-off tests indicated that post-year 2000 dates could not be entered either manually or automatically (via. the RS485 link) into the system. In all cases the system date reverted to the (pre-year 2000) date of testing. The vendor has indicated that the cause resides in the firmware. However, the vendor categorically states that this does not mean that the system is not year-2000 compliant. What was the Solution The inability to program post-year 2000 dates into the control units creates a dilemma: 1) Just because the firmware prevents post-year 2000 dates from being programmed into the control units does not mean that the units are not compliant. Therefore, the question arises "is it worth changing firmware versions just to allow post-year 2000 dates to be entered (for testing purposes)?" 2) If the units are non-compliant how will problems manifest themselves? The solutions are: 1) Do nothing but develop contingency plans. 2) Replace the entire system. This is unlikely given the cost of the system and the extent to which the system has been integrated into the company's infrastructure. Consequences for the SYSTEM Erroneous Result Consequences of failure to the BUSINESS The BEMS controls many items that improve the working environment, for example, air-conditioning and heating units. Should these fail, working conditions may become unbearable during the summer and winter months respectively and perhaps breach HSE regulations.
Equipment Type Industry Sector PC or Computer based Yes Case 55 Building Mgmt Sys ALL System Age 3 Application Building Management system and Lighting Management system Description of the Problem No problem experienced - non-compliance issue picked-up before problem arose. Interface between BMS and other building systems it monitored/controlled. How was it Identified Audit of systems / discussion with suppliers What was the Solution Upgrade of software and PCs, patch for operating system Contingency includes introduction of manual over-rides for plant Consequences for the SYSTEM System Stops Consequences of failure to the BUSINESS Not catastrophic but seriously inconvenient in term of efficient monitoring and control of the building systems
Equipment Type Industry Sector PC or Computer based Yes Case 56 Complex Process Manufacturing Application Component Placement Machine in Surface Mount Assembly of electronic components Description of the Problem User believes that the machine may stop working but the vendors is going to provide a fix. How was it Identified Vendor reports that the machine is not compliant. What was the Solution The vendor is going to provide a complete new PC to replace the original that is actually embedded into the machine. Consequences for the SYSTEM System Stops Consequences of failure to the BUSINESS Impact would be serious if the machine stopped. Production capacity would be reduced
Equipment Type Industry Sector PC or Computer based Yes Case 57 Complex Process Manufacturing System Age 5 years Application Surface mount assembly machines in electronics assembly Description of the Problem Non-compliant according to manufacturer. Built in PC is not compliant. It has been found that the use of the date is for date tagging of program files. The machine will operate normally with the exception of the files saved to disks (floppy) will have 1900 rather than 2000. This effects only the file attributes. How was it Identified By asking the manufacturer if the machine is compliant. What was the Solution No further action is to be taken because 1900 obviously means 2000 Consequences for the SYSTEM Cosmetic Consequences of failure to the BUSINESS Minor process issue
Equipment Type Industry Sector PC or Computer based Yes Case 58 Complex Process Manufacturing System Age Unknown Application Chemical Milling Plant. The system consists of: - Three identical processing Lines (1,2 and 3), - An effluent control system, - A remote PC station for system monitoring / mimicking - A computer system which manages the process data database. Description of the Problem The application software running on the PCs, is definitely not compliant and will no longer be supported by the Vendor. How was it Identified - All relevant documentation was searched for reference to date usage; - A request was sent to the supplier for a compliance statement; - Identified status and location of software back-ups; - System visit to check for undocumented elements and retrofits; - Full system test What was the Solution The system is being fully upgraded to achieve compliance. Consequences for the SYSTEM Erroneous Result Consequences of failure to the BUSINESS Failure of the control system would have Health & Safety implications, which would result in the line being shutdown.
Equipment Type Industry Sector PC or Computer based Yes Case 59 Complex Process Manufacturing System Age 9/10 years old Application A Robotic Wing Router which is a computer-controlled six-axis industrial robot. Description of the Problem The system has an MSDOS-based computer embedded within it for disk and file handling operations. This accepts dates in the format dd-mm-yy, but displays them as dd-mm-yyyy. For example, entering 31-12-99 would display 31-12-1999 How was it Identified Discussions have taken place with the risk owner, the operator and the system programmer in order to establish whether the system uses the date and in what manner. Also the documentation supplied with the equipment has been thoroughly analysed. What was the Solution The date on the system's computer may be manually reset on the 1st January 2000 Consequences for the SYSTEM System Stops Consequences of failure to the BUSINESS In its present configuration, the date is not used. However, if it were to be connected to the site's network then there may be problems with downloading date-related build instructions. This may manifest itself in being unable to use build files after a certain date. Other Whilst the date in this system was clearly visible and was shown to be non-compliant, in it's current configuration the non-compliance was not found to be an issue.
Equipment Type Industry Sector PC or Computer based Yes Case 60 DCS Manufacturing System Age 10 Application Works Energy monitoring system Description of the Problem Statement from manufacturer How was it Identified Statement from manufacturer What was the Solution Upgrade to hardware and software and subsequent testing Consequences for the SYSTEM System Stops Consequences of failure to the BUSINESS Serious consequences on works fuel distribution and control
Equipment Type Industry Sector
PC or Computer based Yes
Case 61 DCS Manufacturing
System Age 5
Application
Measuring thickness of steel strip
Description of the Problem
If the computer rolls over with power off, when it is
next powered up, its BIOS date is 4 Jan 1984. If it
rolls over with power on but is subsequently powered
down and back up, the same date is returned i.e. 4
Jan 1984. This only occurs on roll over from 31 Dec
1999 to 1 Jan 2000.
This problem has been identified on several other
computerised systems.
How was it Identified
Information received from vendor
What was the Solution
By setting the date correctly once in the new century
(e.g. by use of DOS date command), the problem is
overcome. A BIOS fix is also available.
Consequences for the SYSTEM
System Stops
Consequences of failure to the BUSINESS
Wrong date displayed on terminal and any printouts
from system.
Other
Original information from vendor suggested an
expensive fix would be required. Subsequent
investigations proved that this
problem could be fixed quite easily and inexpensively.
Equipment Type Industry Sector PC or Computer based Yes Case 62 DCS Manufacturing System Age Unknown Application Wire Loom Testers. This is a stand-alone system, which is not connected to any computer network. It performs electrical continuity tests on aircraft wiring looms. Description of the Problem On rollover, the PC attached rolls to 00, but the certificates printed out for the customer show the date as being in the year 100 How was it Identified Performing rollover tests on the PC identified the problem What was the Solution The PC and its software are to be replaced with a compliant version. Consequences for the SYSTEM Erroneous Result Consequences of failure to the BUSINESS The system is unable to produce valid certificates for the customer. The customer will reject invalid certificates as they form part of the contract for the aircraft. Consequently, aircraft delivery will be stopped. Other Whilst the rollover showing the date as being the year 100 on the printouts and the system still performed correctly, the printouts were unacceptable from a contractual point of view.
Equipment Type Industry Sector PC or Computer based Yes Case 63 DCS Manufacturing System Age Unknown Application Pipe Bending System is designed to bend pipe-work in a number of dimensions, copying that of an original pro-forma. Description of the Problem - DOS in the PC used by the system presents a 2-digit date field to application and real-time software. Exactly how the software would cope with this is unknown. Due to the fact that all the associated PC's are older 486 systems, the likelihood of failure is increased. - More than one element within the system is aware of the date. How was it Identified - A detailed investigation was undertaken to identify date usage within the system. - A request was sent to the supplier for a compliance statement. - Searches were performed on the Internet for further detail on system elements. - Identified equipment status and location of software back-ups. - System visit to check for undocumented elements and retrofits. - Full system test What was the Solution The PC used by the system is to be replaced with a compliant version Consequences for the SYSTEM System Stops Consequences of failure to the BUSINESS System failure and the loss of being able to determine service intervals. Failure of this system would mean the majority of pipe-work having to be contracted-out, resulting in inevitable delays, and would be counter to the business strategy of becoming a centre of excellence. The impact of failure on the business would be heightened, due to the broad range of products involved.
Equipment Type Industry Sector PC or Computer based Yes Case 64 Fire Control ALL System Age 6 years Application The system is a fire detection system not connected to the local fire brigade. It comprises a number of outstations, fire panels with battery backup connected to two 80486-based computers by means of an RS485 link. Both the computers and fire panels contain history logs. Description of the Problem Centralised PC failed to auto-roll into millennium. Also, 1 model of fire panel refused to allow leap-days to be set. The problem with leap-days was already known to the manufacturer as being caused by the version of the firmware - there is no current solution available. The critical dates are 01.01.2000 and all leap-days. How was it Identified A full range of power on and power off tests were conducted on the computers and fire panels. It was found that in the case of the computers, the power off century rollover test resulted in the date 4th January 1980 being displayed once power had been restored. In the case of the fire panels it was found that although it was not possible to manually set the date to 29th February <leap year> and wait for the internal clock to rollover to 1st March <leap year> the clock did rollover to the 29th February <leap year> when originally set to er, the clock correctly rolled over to 1st March <leap year>. What was the Solution There are two solutions: 1) The computers. These must be replaced with compliant alternatives. 2) The fire panels. The solution for these is "do nothing". However, care must be taken to ensure that there is no need to manually set the date to the 29th February <leap year>. Consequences for the SYSTEM System Stops Consequences of failure to the BUSINESS Possible legal implications if fire were to occur after date corruption had entered the system, for example, no history log.
Equipment Type Industry Sector PC or Computer based Yes Case 65 Fire Control ALL System Age 3 Application Fire control Description of the Problem No problem experienced - non-compliance issue picked-up before problem arose. Graphic History software and PC non-compliant. Operating system non-compliant How was it Identified Audit of systems / discussion with suppliers What was the Solution Upgrade of software , operating system and PCs Consequences for the SYSTEM System Stops Consequences of failure to the BUSINESS Not catastrophic but lack of enhanced graphical presentation of location of fire and fire alarm history would have an effect on the management of this safety element
Equipment Type Industry Sector PC or Computer based Yes Case 66 Fire Control Process Application Fire Station Alarm Monitoring System. System provides the fire brigade with information regarding the state of alarms of critical systems. Control of lighting and motorised doors is also possible through this system. Description of the Problem Problems were experienced with the Visual Basic platform on which the monitoring software runs. The system will have incorrect knowledge of the day of the week post 31/12/99, and will be unable to recognise 29 February 2000. How was it Identified The site alarm computer system was classified as date sensitive following; visual examination of the system, technical discussions with maintenance staff, study of operation manuals and discussions with the originator and translator of the program software in its present form. Rollover tests were then carried out, using TF2000, for the dates; 31/12/1999 and 28/02/2000. What was the Solution 1) Replacement of PC with Y2K compliant version. 2) Replacement of Visual Basic platform with Y2K compliant version. 3) Installation of operating system necessary for latest version of Visual Basic. 4) Amendment of custom code as necessary to run on new platform. Consequences for the SYSTEM System Stops Consequences of failure to the BUSINESS Incorrect knowledge of the days of the week will lead to incorrect identification of silent and normal hours. Failure to recognise leap day will lead to system crash. Both of the above constitute safety risks. If the operator is not aware of computer errors, incorrect action could be taken by fire brigade control staff. This could use remove resources subsequently required for a genuine alarm/incident.
Equipment Type Industry Sector PC or Computer based Yes Case 67 HVAC Manufacturing System Age 8 years Application The system comprises: (a) a centralised PC (with the appropriate software) that monitors and controls the operating parameters of both a boiler management system and microprocessor-based out stations, (b) local area network that connects the outstations and boiler systems to the PC via. networked hubs, [c] portable hand-held computers that are used in the programming of the outstations with, for example, local operating characteristics (d) air-conditioning Description of the Problem While conducting the tests it was found that when power was removed from the outstations and subsequently re-applied, the outstations failed to recognise leap years. As a result of these omissions the history logs held in the central PC became corrupt ed. For example, if the PC was expecting data for the 29th February 2000 it received data (from the outstations) for what the outstations believed to be the 1st March 2000 (since the 29th February had been "lost"). How was it Identified A series of (operational) power on and power off tests were conducted. It was the power off tests that identified the problem. What was the Solution There are two possible solutions (excluding the "do nothing" option): 1) Upgrade the firmware versions of the out-stations 2) Replace the system software. Consequences for the SYSTEM System Stops Consequences of failure to the BUSINESS The system would activate (or deactivate) at various times during the year. Given that there are legally defined minimum working conditions, it could be argued that should the temperature fall below the legally prescribed minimum, Unions may refuse to allow their members to work. Clearly, the effects on the business would be catastrophic.
Equipment Type Industry Sector PC or Computer based Yes Case 68 Logging / Monitoring Manufacturing System Age Unknown Application The Hydraulic Particle Count Analysis System is used to analyse hydraulic fluid from aircraft systems for particles, as an indication of breakdown in component parts. Description of the Problem After the Y2k rollover the system reverts to a date of 1/1/84 which is entered in all the printed-out reports. How was it Identified Full rollover tests were performed on the system What was the Solution The PC is to be replaced with a compliant version. Consequences for the SYSTEM Erroneous Result Consequences of failure to the BUSINESS Unable to print the correct date on the reports generated. For instances where the test result print-out is part of an audit trail, and must therefore be kept to verify correct procedures and that the Aircraft was safe for flight, then incorrect date on the PC due to failure of rollover may invalidate the print-out from a technical/legal standpoint.
Equipment Type Industry Sector PC or Computer based Yes Case 69 Logging / Monitoring Manufacturing System Age Unknown Application This system is found in the automotive industry and is concerned with the "just-in-time" manufacture of airbags. The assembly line is made up of a number of stations. The action carried out at each station is controlled by a dedicated PLC which operates independently of all other PLCs. The whole line is controlled via a main line computer which carries detailed information about the product being assembled and the route map through line, and serves as the link between the assembly line and a network based database. Description of the Problem The reference date is used for comparison against the manufacturing date of components that are included in the assembly. It was suspected that date comparisons would perform correctly and tests revealed that the PLC performing this comparison performed correctly. Further tests revealed that another part of the assembly line suffered a different date related problem which involved the current production date. The problem was found to be the result of converting the year data (100) into two digits (YY) resulting in the printed label containing :0 as representation of the year 2000. It was found that products carrying labels with year :0 are rejected as a result of invalid year code. How was it Identified System diagrams and test schedules based on BSI PD 2000-1 were designed. The main purpose of each test was to identify date-related problems (throughout the production line) during the transition from 1999 to 2000 and other dates including leap year detection. What was the Solution The date handling routine in the label printing software was modified to represent the year 2000 as 00. Tests were carried out to verify this and found that the a fault was again registered. This was traced to the PLC code which compared the year code on the label (00) to the year code in the MDT (100). Therefore a further modification was carried out on the data received from the MDT to represent the year 2000 as 00. Consequences for the SYSTEM Erroneous Result Consequences of failure to the BUSINESS Loss of production on three assembly lines.
Equipment Type Industry Sector PC or Computer based Yes Case 70 Logging / Monitoring OTHER Application Measures and records personal external dose information for those working in radioactive areas. Entry/exit records are date/time stamped and are stored in a database. Description of the Problem 1) The real time clock within the PC will not roll over correctly. As a result of this: Dose records over a given range will total incorrectly; Reader and software records will be incorrectly date stamped. 2) DBU software will rollover to 1900. This will result in the loss of some dose records, making over exposure of some operators possible. How was it Identified 1) Visit site and examine equipment. 2) Review manuals to understand component operation. 3) Investigate PCs and software, including supplier/manufacturer contact. The conclusion that the PC was non-compliant lead to further testing. What was the Solution 1) Replace the PC used for the IDR software with a fully Year 2000 compliant model. Consequences for the SYSTEM Erroneous Result Consequences of failure to the BUSINESS Incorrect dose records would cause the regulator to take action, possibly closing the facility until it could be proved that corrective actions had been successfully implemented. Possible legal costs and personnel injury damages. Other The problems relating to the failure of this system are essentially regulatory in nature.
Equipment Type Industry Sector PC or Computer based Yes Case 71 Weighbridge Manufacturing System Age 10-15 years Application Weighbridge control system Description of the Problem Associated PC logging/control system fails at rollover How was it Identified Standard rollover test What was the Solution Replace PC/system Consequences for the SYSTEM Erroneous Result Consequences of failure to the BUSINESS Basic weighbridge function still OK but logging, ticket production, etc lost. Possible statutory implications re. overloaded vehicles, control of waste material leaving site, etc. Manual workaround possible but additional resource required.
Equipment Type Industry Sector PC or Computer based Yes Case 72 Train Describer. Rail Transport Application Provides information about locations of train services to signallers and other rail staff. The output is used to update a train position model which places each train's unique description (headcode) on a schematic representation of the rail network. Description of the Problem The train describer computer is non-compliant. The system software clock stores date with a 2-digit year, however it prints dates with 4-digit years by using the prefix '19' in output to the printer. On start up the system will accept dates in the range 10/10/84 to 31/12/99. Dates outside this range will be rejected as invalid. The system will rollover to '00' if left powered up. However, in the event of a failure it will not be possible to restart the system and enter the correct date after 31/12/99. The day of the week will be incorrectly calculated after the 2000 leap day, so the describer may refer to the wrong timetable. How was it Identified Investigation steps included: Site visits; Discussions with suppliers, including reference to documentation; Inspection of source code for the system software real time clock i.e. RTIME and DATE. What was the Solution Modifications are possible to make the system compliant. However, it is reasonably old and difficult to maintain, so replacement is preferable. Consequences for the SYSTEM System Stops Consequences of failure to the BUSINESS Loss of reputation. Customers claiming refunds on tickets where trains running at incorrect times, late or not at all. /PRE>Equipment Type Industry Sector PC or Computer based Yes Case 73 Terminal interface OTHER Application Programming terminal interface. Description of the Problem System is very old and is unable to recognise any dates beyond 31/12/99. How was it Identified Rollover testing was carried out on the system. What was the Solution Upgrades are not possible as the system is too old. However, failure is not acceptable so the system must be replaced. Consequences for the SYSTEM System Stops Consequences of failure to the BUSINESS Loss of profit if production stops. Other The programming terminal is an early version of an industrial portable PC.Equipment Type Industry Sector PC or Computer based Yes Case 74 Data loggers Manufacturing Application Data loggers - Industrial PC used to archive information Description of the Problem PC BIOS cannot handle the rollover to 01/01/00. It will not be possible to archive information. How was it Identified Rollover tests using the TF 2000 scanner. What was the Solution Upgrade BIOS. Consequences for the SYSTEM Erroneous Result Consequences of failure to the BUSINESS If there is a fault in a manufacturing process, it will not be possible to review archived information.Equipment Type Industry Sector PC or Computer based Yes Case 75 meter Maritime Application Custody transfer meter Description of the Problem On 1st January 2000, the custody transfer report screen displays the date 1.1.100. The actual custody transfer forms show 1.1.2000 when printed out. How was it Identified The problem was discovered during testing. What was the Solution The vessels will need to have their custody transfer system software upgraded. This will take place either at planned vessel refit or with the vessel in service. Consequences for the SYSTEM Cosmetic Consequences of failure to the BUSINESS Nuisance to suppliers and buyers when reports and displays show inconsistent dates.Equipment Type Industry Sector PC or Computer based Yes Case 76 Data logger Oil & Gas Application A hand held vibration data logger and PC based software package. Description of the Problem During functional testing and with the date set to 1st January 2000, vibration was monitored using the device and the data downloaded into the PC. The trend was then displayed. The trend normally displayed the last few weeks' data ending with the latest piece of information. As a result of the test, the display became totally nonsensical. When the date was returned to 22/11/97 and the test repeated, the system still failed. How was it Identified The manufacturer claimed that the system was compliant. The problem was discovered during functional testing. What was the Solution The package will be upgraded to a version running under Windows NT, which is claimed compliant Consequences for the SYSTEM Erroneous Result Consequences of failure to the BUSINESS Any planned monitoring and maintenance programme would be severely disrupted by such an error.Equipment Type Industry Sector PC or Computer based Yes Case 77 Fuel dispenser Manufacturing System Age 20+ years Application Automated fuel dispensing system. The system comprises: (1) A coded key system located adjacent to the fuel dispensing hardware and away from buildings for safety reasons . The data stored on the key includes, inter alia, the user's identification and department numbers. (2) A 386-based computer connected to the fuel system via. a modem link and located within an office. On the computer resides logging software that records the key's data, the amount of fuel dispensed and the time and date. This information is subsequently used to bill the appropriate department for the fuel consumed. Description of the Problem The cause of the problem was the system's inability to recognise the century change and other 21st century dates. The designers "fixed" the century part of the year at "19". How was it Identified At first it was assumed that the computer software logged the time and date using its own internal clock. This assumption was made because there was no obvious date functionality within the fuel dispensing system. Additionally, as the system had previously been used at numerous sites all associated documentation had been lost. As the system was over 20 years old, the operators stated that not only was the system unreliable but they had also experienced considerable difficulty in obtaining spare parts. While discussing the cost of a new system with the manufacturer they (the manufacturer) stated that the fuel system did possess a clock that embedded the time and date within the data stream that was passed to the computer. What was the Solution The recommendations to deal with the problem are as follows: 1) Do nothing. If the amount of fuel dispensed is the only important item on the bill then it could be argued that the time and date of the act is immaterial. 2) Workaround, that is, write the correct time and date on the printouts. Since the billing process is paper-based and manual the question of non-compliant (automated) systems interfacing with compliant systems does not arise. 3) Replace the system. This solution will require the company to reappraise its capital investment policy. For example, if the system is due for replacement in, say, 5 years time, it may be replaced at the century change. Consequences for the SYSTEM Cosmetic Consequences of failure to the BUSINESS As far as the bill is concerned non-compliance represents a nuisance and arguably a minor irritation to the system's administrators.Equipment Type Industry Sector PC or Computer based Yes Case 78 transfer system Maritime Application Custody transfer system Description of the Problem On 1st January 2000, the internal clock in the custody transfer meter system will revert back to the date the original PC BIOS was programmed, either 1986 or 1981. This will affect the date time stamp on alarm reports. If alarm reports are archived this will over write previously saved files. How was it Identified The problem was identified during testing. What was the Solution The vessels will need to have their custody transfer system software upgraded. This will take place either at planned vessel refit or with the vessel in service. Consequences for the SYSTEM Erroneous Result Consequences of failure to the BUSINESS The archive will become invalid as files become overwritten.Equipment Type Industry Sector PC or Computer based Yes Case 79 PLC Process System Age 5- 10 years Application Chemical process control, comprising 1 off PLC, and 3 off SCADA systems. The PLC controlled the overall process, and the SCADA system was used for System Mimic, data logging, trending etc, but it had no inherent control of the process. Description of the Problem A system test was performed on the SCADA systems and PC platforms individually, which highlighted some date related problems with the SCADA system. How was it Identified The tests performed on the SCADA system were to manually change the Date/Time to just before the rollover date we were required to check, and then let it roll over in POWER-UP mode, then power it down, and then power it up again to verify if it retained the correct date. What was the Solution Effectively a work around was put into place. As the date functionality was deemed to be Non-Business critical, after the roll-over the system Date would be manually changed, and the system rebooted. Consequences for the SYSTEM Cosmetic Consequences of failure to the BUSINESS Cosmetic for both Business and also SystemEquipment Type Industry Sector PC or Computer based Yes Case 80 SCADA Manufacturing System Age 4 Application Operation & control of gas flare stack Description of the Problem How was it Identified Audit by supplier identified that version of Unix was not compliant What was the Solution This system is to be relocated /modified in year2000 Decision made to roll date back 8years (non compliance date associated )and not spend money to fix .8 Years was to keep leap year in line if system was not immediately replaced Consequences for the SYSTEM System Stops Consequences of failure to the BUSINESS Failure to open the flare stack could cause over pressurisation of gas distribution system including gas holder if gas manufacturing units could not be reduced especially if consumers were to fail due to y2k problems.Equipment Type Industry Sector PC or Computer based Yes Case 81 SCADA Manufacturing System Age approx. 15 years Application Operator interface & display system Description of the Problem Custom firmware fails rollover test. PC platforms also fail. How was it Identified Standard rollover test What was the Solution Replace Consequences for the SYSTEM Erroneous Result Consequences of failure to the BUSINESS Key manufacturing plant constrained in operation. Most major functions operable albeit at reduced efficiency but data logging, etc lost.Equipment Type Industry Sector PC or Computer based Yes Case 82 SCADA Manufacturing System Age 5 years Application Windows based SCADA system for chemical handling plant Description of the Problem The first test was a BIOS rollover test with (unfortunately) the SCADA package running. A failure occurred, causing a `lockup' with a complete lack of response. A manual trip was initiated, however not before an acid spill occurred resulting in a minor environmental problem and a major safety incident. Unfortunately, the company's personnel failed to realise the implications of conducting such a test on an operational plant. Another test, was performed some weeks later on a later version this time with properly prepared test plans, and plant personnel awareness. One function of the tests was for 09-09-99, 0909-1999 and 99-99-9999. These `dates' resulted in the software failing to execute. Note that 99 is often used as end of file indicator. How was it Identified See above What was the Solution Replacement Consequences for the SYSTEM System Stops Consequences of failure to the BUSINESS Dangerous chemical spill Other Testing live systems requires careful forethought and preparation. Always back up data first.Equipment Type Industry Sector PC or Computer based Yes Case 83 Smart Instruments Manufacturing System Age 10+ Application An "electrical continuity tester" (ECT) It is standalone, that is, it is not a part of another system and comprises: 1) a master switching console (MSC) that connects the wiring loom under test to the ECT by means of a 100-way cable. 2) an PC connected to the ECT by means of an RS232 link. This computer contains all the programs required to automate the operation the ECT and record the results of the tests. 3) the ECT itself which is connected to the electricity supply and contains banks of manually operated make or break switches. Description of the Problem The problem that would have been experienced is as follows: On the 30th December 1999 it would not have been possible to set the system's operation for, say, 1st January 2000. The PC would have interpreted the year as 1900 which meant that the license would have been invalid which in turn meant that the system would refuse to operate. Given that the system would fail to operate it is not possible to identify any further effects of non-compliance. How was it Identified The PC-based problem was discovered by implementing a series of power on and power off tests. The following power-off tests were the main cause of failure.: a) Century roll over b) leap year (rollover) tests (28th February <leap year> to 29th February <leap year> to 1st March <leap year>) The "license expiry" was determined by entering into discussions with the system's manufacturers who insisted on undertaking their own tests before providing a reply! What was the Solution Replacement Consequences for the SYSTEM System Stops Consequences of failure to the BUSINESS Given that the license would prevent the system from operating it would be logical to assume that the product could not be tested and therefore could not be sold. In the short term the credibility of the business would suffer. In the medium term customers may impose (financial) penalties because the product had not been delivered on time. In the longer term the business may cease trading.Equipment Type Industry Sector PC or Computer based Yes Case 84 Stand alone instrument Manufacturing System Age 10 Application Level and flow monitoring of waste acid treatment plant Description of the Problem Problem experience with some versions of firmware. If the unit rolls over any year (i.e. not Y2k specific) with the power supply off, on power up, the display is blank and the keyboard locked so that the device will not operate. How was it Identified During off line testing in the workshop. What was the Solution A known compliant version of the firmware has been installed. Long term, the unit will be replaced. Consequences for the SYSTEM System Stops Consequences of failure to the BUSINESS Inability to treat acid, resulting in shutdown of plant. Other Users of these instruments would need to test compliancy of all versions of firmware. In this case, it was the latest version that exhibited the problem.Index
Milling, 25, 35
A monitor, 11, 19, 28
Access control, 32 Monitor, 21
Access Control, 3, 6, 31 monitoring, 4, 11, 16, 22, 30,
acid treatment, 52 34, 35, 36, 40, 46, 52
air conditioning, 14, 31 Monitoring, 3, 14, 15, 16, 18,
Air Conditioning, 12, 13 26, 40, 41, 42, 43
Audio, 21
P
B packet switching, 17
BEMS, 33 petrochemical, 9
BMS, 31, 34 Photocopier, 20
Boiler, 12 PLC, 3, 24, 25, 42, 48
Building Mgmt Sys, 3, 7, 31, 32,
33, 34 R
Recorder, 15
C Robot, 25
Car Park, 17 Robotic, 36
Card access, 6
Chart recorder, 18 S
Chemical, 35, 48 satellite, 16
CNC, 25 SCADA, 3, 26, 27, 28, 48, 49, 50
communications, 14, 17, 19, 33 Scanning, 21
Custody transfer, 45, 48 security, 3, 4, 31
Smart instruments, 28
D Smart Instruments, 3, 29, 51
data logger, 46 Stand Alone Instrument, 3, 30
Data Logger, 18 Surface mount, 35
Data loggers, 45 Surface Mount, 34
Date coding, 8 Swipe card, 32
DCS, 3, 9, 36, 37, 38
Defibrillator, 30 T
density analyser, 29 tape machine, 20
detector, 23 telephone, 22, 29
Train Describer, 44 F
fire alarm, 11, 39 U
Fire alarm, 10 Ultrasound, 21
Fire Alarm, 7, 10, 11 UPS, 30
Fire Control, 3, 10, 11, 39, 40
fuel dispensing system., 47 V
Fuel Pump, 23 vibration, 46
Vibration, 19
G
Gas, 9, 23, 29, 46 W
gas flare stack, 49 Weighbridge, 43
Weighing, 22, 28 H welding, 26
HVAC, 3, 12, 13, 14, 41
I
Intruder Panel, 6
L
Logging, 3, 4, 15, 16, 41, 42,
43
M